Contouring Survey
Introduction :
Molding is, essentially, a leveling activity. The gear are the equivalent for leveling and shaping.
The fundamental goal of shaping is to decide the focuses on the ground having the equivalent decreased level. The shape lives join the purposes of same rise straightforwardly or by insertion strategy. It gives the geographical highlights of the ground, looking at changed shape lines of various heights for a shut territory. In view of the geographical highlights, counts for building tasks can be completed.
There are distinctive strategy for drawing such shut or open form lines inside a particular territory.
The fundamental goal of shaping is to decide the focuses on the ground having the equivalent decreased level. The shape lives join the purposes of same rise straightforwardly or by insertion strategy. It gives the geographical highlights of the ground, looking at changed shape lines of various heights for a shut territory. In view of the geographical highlights, counts for building tasks can be completed.
There are distinctive strategy for drawing such shut or open form lines inside a particular territory.
What is contouring in Surveying?
Forming in reviewing is the assurance of rise of different focuses on the ground and fixing these purposes of same flat positions in the shape map.
To practice vertical control leveling work is completed and all the while to practice even control chain study or compass study or plane table overview is to be done.
On the off chance that the theodolite is utilized, both level and vertical controls can be accomplished from a similar instrument. In view of the instruments utilized one can arrange the molding in various gatherings.
Methods of Contouring Survey :
- Direct method
- Indirect method
Direct Method of Contouring :
It comprises in discovering vertical and level controls of the focuses which lie on the chose shape line.For vertical control leveling instrument is regularly utilized. A dimension is determined to a telling position in the region in the wake of taking fly dimensions from the close-by seat mark. The plane of collimation/tallness of instrument is found and the required staff perusing for a shape line is determined.The instrument man asks staff man to climb and down in the territory till the required staff perusing is found. A surveyor builds up the even control of that point utilizing his instruments.After that instrument man guides the staff man to another point where a similar staff perusing can be found. It is trailed by setting up flat control.In this way, a few points are set up on a form line on a couple of shape lines and reasonably noted down. Plane table study is preferably appropriate for this work.After required focuses are set up from the instrument setting, the instrument is moved to another point to cover more region. The dimension and overview instrument need not be moved in the meantime. It is better if both are adjacent to impart effectively.For getting speed in leveling a few times hand level and Abney levels are additionally utilized. This strategy is moderate, repetitive however exact. It is appropriate for little zone.
Indirect Method of Contouring :
In this methodology, levels are taken at some picked concentrations and their measurements are lessened. Along these lines in this technique level control is developed first and after that the components of those centers found.
In the wake of finding the spotlights on the course of action, diminished measurements are stepped and structure lines are embedded between the picked centers.
For choosing focuses any of the accompanying techniques can be utilized:
Technique for squares
Technique for cross-area
Outspread line technique
In the wake of finding the spotlights on the course of action, diminished measurements are stepped and structure lines are embedded between the picked centers.
For choosing focuses any of the accompanying techniques can be utilized:
Technique for squares
Technique for cross-area
Outspread line technique
Method of Squares :
Normally utilized size of square changes from 5 m × 5 m to 20 m × 20 m. Dimensions of all lattice focuses are built up by leveling. At that point framework square is plotted on the illustration sheet. Diminished dimensions of network focuses checked and shape lines are drawn by addition
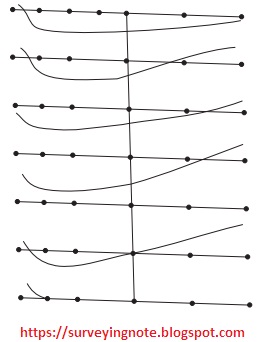
Method of Cross-Section
In this technique cross-sectional focuses are taken at ordinary interim. By leveling the decreased dimension of each one of those focuses are built up. The focuses are set apart on the illustration sheets, their diminished dimensions (RL) are stamped and shape lines interjected.
 |
| Cross Sections |
Figure 2 demonstrates an average arranging of this work. The dividing of cross-area relies on the idea of the ground, size of the guide and the shape interim required. It changes from 20 m to 100 m. Closer interims are required if ground level fluctuates unexpectedly.
The cross-sectional line need not be dependably be at right edges to the primary line. This strategy is in a perfect world appropriate for street and railroad ventures.
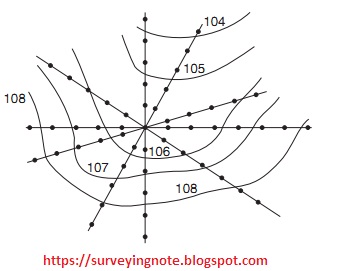
Radial Line Method :
In this technique a few spiral lines are taken from a point in the region. The course of each line is noted. On these lines at chosen separations focuses are checked and levels decided. This strategy is in a perfect world appropriate for bumpy zones. In this study theodolite with tacheometry office is generally utilized.
 |
| Radial line |
For inserting shape focuses between the two points any of the accompanying strategy might be utilized:
(a) Estimation
(b) Arithmetic calculation
(c) Mechanical or graphical method.
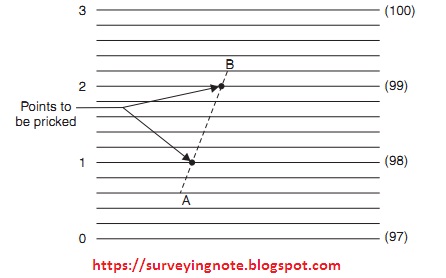
Mechanical or graphical method :
On a following sheet a few parallel lines are drawn at ordinary interim. Each tenth or fifth line is made darker for simple checking. On the off chance that RL of An is 97.4 and that of B is 99.2 m. Expect the base most dim line speaks to 97 m RL and each parallel line is at 0.2 m interims. At that point hold the second parallel line on A.
Pivot the following sheet with the goal that 100.2 the parallel line goes through point B. At that point the convergence of dull lines on AB speaks to the focuses on 98 m and 99 m shapes.
Additionally the form focuses along any line interfacing two neighboring focuses might be gotten and the focuses pricked. This strategy keeps up the precision of math computations in the meantime it is quick.
Additionally the form focuses along any line interfacing two neighboring focuses might be gotten and the focuses pricked. This strategy keeps up the precision of math computations in the meantime it is quick.
 |
| Mechanical or graphical method |
Contouring survey Maps :
A shape maps comprises of form lines which are fanciful lines associating purposes of equivalent height. Such lines are drawn on the arrangement of a region in the wake of setting up diminished dimensions of a few in the zone.
The shape lines in a zone are attracted keeping contrast rise of between two back to back lines steady. For instance, the shape map in fig. 1 indicates shapes in a region with form interim of 1 m. On form lines the dimension of lines is additionally composed.
 |
| Contour map |
Characteristics of Contour Maps :
Form lines should close, not really in the points of confinement of the arrangement.
Generally dispersed form demonstrates level surface.
Firmly dispersed shape shows soak ground.
Similarly dispersed shape shows uniform incline.
Unpredictable forms show uneven surface.
Roughly concentric shut forms with diminishing qualities towards focus (Fig. 1) show a lake.
Around concentric shut forms with expanding esteems towards focus demonstrate slopes.
Form lines with U-shape with convexity towards lower ground show edge (Fig. 2).
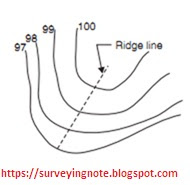 |
| ridge line |
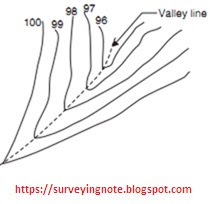 |
| Valley line |
Definition of Contouring survey :
A form or a shape line might be characterized as the line of convergence of a dimension surface with the outside of ground. This implies each point on a shape line has a similar elevation as that of the accepted meeting surface.
Assuming a wretchedness is incompletely loaded up with water and R.L of the water surface is state 60 m, at that point the shore line of this water speaks to 60 m form. Furthermore, if the dimension of water is raised progressively by 1 m, the progressive shorelines speak to 61, 62, 63 m shapes, etc.
The way toward following form lines on the outside of the earth is called molding and the maps whereupon these lines are drawn are called shape maps. A shape map in this manner, gives an ides of the elevations of the surface element just as their relative positions in plan. In this way a shape map fills the need of both, an arrangement and an area.
Contouring survey Interval and Horizontal Equivalent:
Direct and Indirect Methods of Contouring:
Direct Method:
1. The strategy is most exact yet is exceptionally moderate and dreary.
2. It is utilized for little zones where extraordinary precision is wanted.
3. It isn't exceptionally valuable when the around is uneven.
4. The computation work of lessening the dimensions is similarly more since the quantity of focuses in order from one set - up of the dimension is extremely less.
Indirect Method:
1. The technique isn't extremely exact yet is less expensive, faster and less difficult.
2. It is utilized for substantial regions where extraordinary exactness isn't the principle thought.
3. Tacheometric strategy for shaping is for the most part utilized for planning, form plans of bumpy territory. The backhanded technique by cross - segments is utilized in course reviews, for example, a railroad, a channel and so on.
4. Zone in order from one set - up of the tacheometer is more, consequently, the estimation work is less.
Interpolation of Contours:
The way toward dispersing the forms relatively between the plotted ground focuses is named as interjection of shapes. This gets important on account of backhanded molding as just the spot levels are taken in this strategy. The middle of the road forms may likewise be added in direct molding if the span is enormous. While interjection of forms the ground between any two focuses is thought to be consistently inclining.
There are three methods
(i) By estimation,
(ii) By arithmetical calculation, and
(iii) Graphical method.
(i) By Estimation:
The places of the form focuses between ground - focuses are assessed generally, and the shapes are then drawn through these focuses. This is a harsh strategy and is reasonable for little scale maps.
(ii) By Arithmetical Calculation:
Assume An and B are two points at a separation of 30m and the diminished dimensions An and B are 24.32m and 26.90m separately. Accepting the shape interim as 1m, 25 and 26m forms might be added in the middle of An and B. The distinction of level among An and B is 2.58m. The distinction of level among An and 25 and An and 26m shapes is 0.68m and 1,68m individually.
Along these lines the flat separation among An and 25 m shape and that among An and 26 m form
These separations are then plotted to scale on the guide.
(iii) By Graphical Method:
Assume the form interim is 5m , then on a bit of following fabric, various parallel lines divided at 0.5 m (normally one tenth of the shape interim) are drawn, each tenth line being made thick (Fig. 8.11). Assume it is required to introduce forms between two An and B of rises 61.5 m and 72.5m individually.
On the off chance that the reality speak to a height of 60m, at that point the progressive thick lines will speak to 65m, 70m and 75 m and so on. Spot the following fabric so the point An is on the third line from the base. Presently, move the following fabric until B is on the fifth line over the 70m thick line.
The crossing points of the thick lines 1 and 2 speaking to rises of 65m and 70m and the line AB give the situation of the focuses on the 65m and 70m shapes separately and are pricked through on the arrangement with a stick.
Drawing the Contour Lines :
Form lines are drawn as fine and smooth free hand bended lines. Now and again they are spoken to by broken lines. They are connected in either in dark or in darker shading. An illustration pen gives a superior line than a composition pen, and French bends ought to be utilized however much as could be expected.
Each fifth shape is made thicker than the rest, the height of forms must be written in a uniform way either on the higher side or in a hole left in the line. At the point when the shape lines are extremely long the rise are composed at a few places along the form. On account of little scale maps, it is adequate to figure each fifth form.
A form inclination might be characterized as a line joining the focuses on various shapes along a similar slope.
Demonstrate a form map on which the shape lines are at 2m interims. The ground is inclining an upward way from A to B. Assuming it is required to follow the way of a street with a decision inclination of 1 out of 30 from the beginning stage An on the 80 m shape line Since the form interims is 2m and the slope 1 out of 30, the even separation between progressive focuses on successive shapes is 60m (2 x 30).
With An as focus and range equivalent to 60m draw a curve cutting the 82m shape at 1. With 1 as focus and a similar sweep, draw a bend meeting the 84m form at 2, etc for progressive shapes. Join these focuses which lie on the ideal inclination. It might be noticed that every one of the curves depicted will meet the following shape at two points viz 1 and I, 2 and ii, 3 and iii and so on at 82, 84, 86. meter form and so on and the focuses following the ideal course, for example, 1, 2, 3, and so forth. ought to be joined
Discovering Volume of Earth and Capacity of a Reservoir from Contour Lines
The volume of earth work and limit of a supply might be determined by treatment of shape lines. This technique is just rough as in managing shape lines we need to expect that the outside of the ground inclines consistently structure one form to the following and much of the time this supposition that is mistaken. Anyway adequate precision can be accomplished if the shapes are situated with an interim little enough to record reflect highlights of the ground.
After readiness of the shaped arrangement of the specific site , the region encased by each form line is estimated by a planimeter, knowing the vertical separation between the first and the second shape lines (the form interim) and their regions , Volume of earth work or water between them might be determined shrink by trapezoidal equation or by some other recipe.
Let A1, A2, A3 and so on = The territories inside progressive form in sq. meters.
d = the form interim in meters
Each fifth shape is made thicker than the rest, the height of forms must be written in a uniform way either on the higher side or in a hole left in the line. At the point when the shape lines are extremely long the rise are composed at a few places along the form. On account of little scale maps, it is adequate to figure each fifth form.
A form inclination might be characterized as a line joining the focuses on various shapes along a similar slope.
Demonstrate a form map on which the shape lines are at 2m interims. The ground is inclining an upward way from A to B. Assuming it is required to follow the way of a street with a decision inclination of 1 out of 30 from the beginning stage An on the 80 m shape line Since the form interims is 2m and the slope 1 out of 30, the even separation between progressive focuses on successive shapes is 60m (2 x 30).
With An as focus and range equivalent to 60m draw a curve cutting the 82m shape at 1. With 1 as focus and a similar sweep, draw a bend meeting the 84m form at 2, etc for progressive shapes. Join these focuses which lie on the ideal inclination. It might be noticed that every one of the curves depicted will meet the following shape at two points viz 1 and I, 2 and ii, 3 and iii and so on at 82, 84, 86. meter form and so on and the focuses following the ideal course, for example, 1, 2, 3, and so forth. ought to be joined
The volume of earth work and limit of a supply might be determined by treatment of shape lines. This technique is just rough as in managing shape lines we need to expect that the outside of the ground inclines consistently structure one form to the following and much of the time this supposition that is mistaken. Anyway adequate precision can be accomplished if the shapes are situated with an interim little enough to record reflect highlights of the ground.
After readiness of the shaped arrangement of the specific site , the region encased by each form line is estimated by a planimeter, knowing the vertical separation between the first and the second shape lines (the form interim) and their regions , Volume of earth work or water between them might be determined shrink by trapezoidal equation or by some other recipe.
Let A1, A2, A3 and so on = The territories inside progressive form in sq. meters.
d = the form interim in meters
Contouring Survey Draw Contours Lines Watch :
QUESTION AND ANSWER
1 The intersection of a level surface
with the ground surface is
= contour line
2 The vertical distance between any
two consecutive contours is
= contour interval
3 The horizontal distance between any
two consecutive contours is
= horizontal equivalent
4 The higher values inside the loop
indicates
= hill
5 The lower values inside the loop
indicates
= depression
6 The line joining points of equal
elevation is
= contour line
7 A contour line intersects a ridge
line or valley line
= perpendicularly
8 The contour interval for a
particular map is
= kept constant
9 When contour lines touch one another
at a particular zone indicates
= vertical cliff
10 The contour interval is inversely proportional
to the
= steepness of the area
11 When a contour interval is fixed
between 0.25 and 0.50 m it indicates
= a flattish slope
12 The alignments of highways are generally taken along
= a ridge line
13 When contours of different
elevation cross each other, it indicate
= overhanging cliff
14 When consecutive contour lines run
close together, it indicate
= steep slope
15 A series of closely spaced contour
lines is represented as
= a steep slope
16 The suitable contour interval for a
map with scale of 1 : 1000 is
= 2 m
17 In direct method of contouring the
process of locating points lying on a contour is
= vertical contour
18 The intersection method of detailed
plotting is most suitable
= hilly area













0 Comments:
Post a Comment